Search Results for ‘uce’
I think the best possibility is to work on upgrading VSSUT, Burla (formerly, UCE Burla) to an IIEST. UCE Burla alumni is fully supportive of this. In general, such a proposal has and will continue to have support from all circles of Odisha. Also, the CM has in the past written to Delhi about upgrading this.
To do this first the state government needs to be pushed to give a one time allocation of a significant amount (say 100 crores) to improve the infrastructure. In addition the faculty size needs to be increased to be at the level of the colleges mentioned below. Simultaneously there should be a campaign to convince the central government to upgrade it to an IIEST.
The Congress MP from Sambalpur should do all he can for this.
For some background on IIESTs see http://164.100.47.132/LssNew/psearch/QResult15.aspx?qref=89897. Following are screen capture of that page.
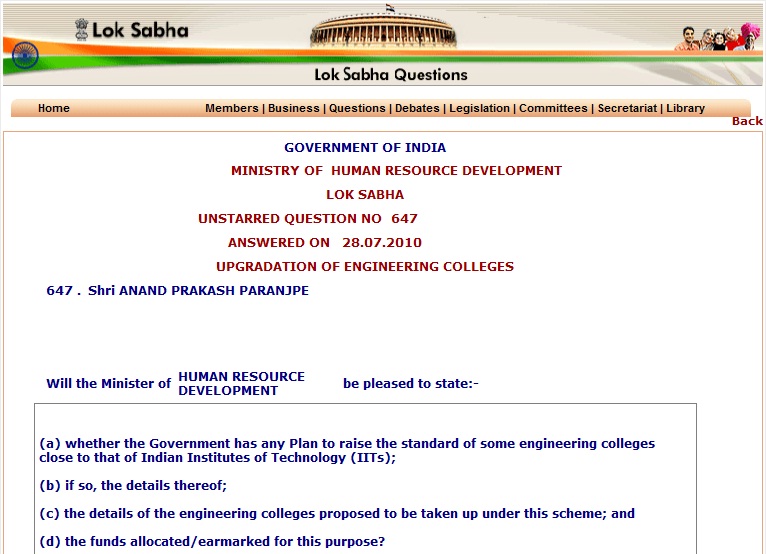

August 18th, 2010
Following is a from a PTI report in ibnlive.com.
National Institute of Technology-Rourkela and Vedanta Aluminium today signed an Mou to develop an environment-friendly technology.Vedanta will finance NIT-R to develop a cost-effective method for neutralisation of red mud and removal of poisonous heavy metals like arsenic, zinc and cadmium and to upscale the technology to industrial scale. …
Disposal of red mud, the waste product of aluminium manufacture had been bothering aluminium industries and governments and causing environment hazard. The disposal methods being followed has been creating problem of contamination of ground and surface water.Kumar said red mud mostly contain 50 per cent of iron ore and the aluminium industries want to reduce the level to zero.
August 12th, 2010
Following is an excerpt from a report in tathya.in.
Debi Prasad Mishra, Minister Higher Education introduced the Centurion University of Technology and Management Orissa Bill-2010 here on 31 July in the Assembly.
According to the Bill, the university will have its campus at Paralakhemundi, which has sixty acres of land and at least 10,000 square meters will be available in the form of buildings and ancillary infrastructure.
The university shall be unitary, self-financed and it is established to provide advanced knowledge in branches of Engineering & Technology, Medical Science & Genetics, Humanities & Social Science, Management, Law, Vocational Education & Training, Tribal and Development Studies.
… The Governor of Odisha will be the Visitor of the university and will preside over the convocation of the varsity.
The Visitor will have sweeping powers and can call for any papers or information relating to the affairs of the university.
The Chairman of the Trust will be the President of the varsity, where as the university will have Vice Chancellor, Pro-Vice Chancellor and other regular functionaries.
The Bill will be taken up for discussion in the House next week, said sources.
July 31st, 2010
Its website is http://inspire-dst.gov.in/. Following are important links:
Following are some excerpts from the application form.
Genesis of INSPIRE: Global competitiveness in the changing global knowledge economy calls for expansion and right-sizing of the Research and Development base of the country. Need for
special interventions for attracting youth to study of natural sciences and careers with research is recognized. Innovation in Science Pursuit for Inspired Research (INSPIRE) is a Programme launched by the Government of India to strengthen the National Science and Technology base. It is being implemented by the Department of Science and Technology (DST).
About INSPIRE: Programme includes three components namely Scheme for Early Attraction of
Talents for Science (SEATS), Scholarships for Higher Education (SHE) and Assured Opportunity for Research Careers (AORC). The Scheme SHE is focused on attraction of talent to study of natural/basic sciences at the bachelor and master’s level education. SHE is currently limited to support for educational programmes at B.Sc., B.Sc. (Hons), M.Sc. and integrated master’s level course in sciences leading to MSc in any branch of natural and basic sciences namely mathematics, statistics, physics, chemistry, earth sciences and life sciences.
Call for Applications: Applications are invited from eligible candidates for `Scholarship for
Higher Education (SHE)’ component of INSPIRE. Total of 10,000 scholarships are available
annually under SHE starting April 2008. The scholarships are limited only to the candidates
studying courses in natural/basic sciences (B.Sc., B.Sc. (Hons), integrated M.Sc.) in any one of the recognized institutions in India. Eligibility criterion for the scholarships are a) performance in
board examinations within the cutoff threshold (of top 1%) for each state or central board
examination at the class X and class XII level and/or b) performance in any of the specified
competitive examinations within stipulated cut off ranks. The eligible applicant must be already
enrolled into degree level education in natural/basic sciences in any of the recognized institutions
in India.
Criteria for Eligibility for SHE:
a) Based on Performance in Board Examinations: The candidates should have obtained
aggregate marks in the top 1% in the board examination at both class X and XII levels. For
example, the candidates applying for INSPIRE Scholarship 2008 should have secured marks
within the top 1% in class X in the year 2006 and class XII in 2008 in the respective board
examinations and should have joined a degree course leading to B.Sc. or B.Sc. (Hons) or
integrated M.Sc. in natural/basic sciences in any institution in India. Cut-off marks for various
board examinations conducted in the years 2006 and 2007 for class X and corresponding year
of 2008 and 2009 for class XII are listed in Table 1. The cut-off marks of various Board
Examinations conducted in the years 2008 for Class X and 2010 for Class XII are being compiled and shall be up-loaded in Website in due course. Candidate securing top 1% marks only in class XII board examination can also submit the application form.
b) Based on Performance in Competitive Examinations (specified in Table 2).: Performance
within the top 10,000 ranks in Joint Entrance Examination of IIT, AIEEE (Engineering) and CBSE medical and joining degree level courses in natural/basic sciences in any recognized Indian
institution. The candidate may apply with a valid document of these examinations. The scheme in its current format does not include courses in engineering, medicine, technology and other
professional courses.
c) Based on Performance in Competitive Examinations (specified in Table 3): Clearance of
competitive examinations conducted by institutions listed in Table 3 and all candidates securing
admissions and joining integrated M.Sc/ MS courses in natural/basic sciences conduced by Indian Institutes of Science Education and Research (IISER), National Institute of Science Education and Research (NISER), in Indian Institutes of Technology, Department of Atomic Energy – Centre for Basic Science (DAE-CBS) and University from the academic years 2008-09, 2009-10 ad 2010-11 are eligible. Institutional coverage is being done for this category. Students in this category need not to apply.
Value and Type of Support: Eligible candidates will receive annually scholarship @ total value
Rs.80,000 per candidate. The cash value payable to the SHE scholarship holder is Rs.60,000 per annum. All the SHE scholars are undertake summer time attachment to an active researcher in recognized research centers in the country. A summer time attachment fee of Rs.20,000 will be paid to the mentoring institution for undertaking summer time project.
Duration of the Support: Selected candidates will be supported for a maximum period of five
years starting 1st year course in B.Sc., B.Sc. (Hons) and integrated course leading to M.S. or M.Sc. or the completion of the course, which ever is earlier. Continuation of the scholarship for once selected candidates is based on satisfactory performance of the examinations conducted and certified by the institution imparting education.
Format for Application: All interested and eligible candidates (as per Table 1 for Board
examination based eligibility or as per Table 2 or Table 3 for competitive examination based
eligibility) must apply in the prescribed format written preferable in English & Hindi only along
with attested copy of i) Mark sheets of Class X and Class XII and ii) Endorsement Certificate from Principal of the College/ Director or Registrar of the Institute or University where the applicant is presently enrolled. Candidate may please download this Advertisement and Application Format which is available at the website: www. inspire-dst.gov.in and submit the duly filled-in application with all necessary documents. Applications should be sent by Ordinary Post only within one month from the date of this advertisement in Newspaper and shall be addressed to the Director, National Institute of Science, Technology & Development Studies (NISTADS), Dr K S Krishnan Marg , New Delhi – 110012. The envelope should mention on top “Application for INSPIRE Scholarship – 2008, 2009 and 2010” program. For online submission of application, kindly also visit the Website: www.inspire-dst.gov.in. The online applicants should also submit a hardcopy of the applications with all attested documents.
July 19th, 2010
Following is extracted from multiple sources including http://www.aicte-india.org/excel/29jun/ORISSA.html.
| College |
M.Tech branch |
Number of Seats |
| Mahavir Institute of Engineering & Technology, Bhubaneswar (36) |
Computer Science & Engg |
18 |
| |
Electrical & Communication |
18 |
| DRIEMS, Cuttack (90) |
Computer Science |
18 |
| |
ECE |
18 |
| |
EE (Power) |
18 |
| |
Electronis & Instr |
18 |
| |
IT |
18 |
| Synergy, Dhenkanal (72) |
Computer Science & Engg |
36 |
| |
Electrical & Comm. (VLSI & Embeded System) |
18 |
| |
Electrical & Electronics (Power Electronics & Drives) |
18 |
| Majhighariani, Rayagada (36) |
BioTechnology |
18 |
| |
Mechanical Engineering |
18 |
| East, Bhubaneswar (36) |
Computer Science & Engineering |
18 |
| |
Electronics & Telecommunication |
18 |
| CIPET, Bhubaneswar (54) |
Material Sc & Technology (M.SC) |
18 |
| |
Plastic Engineering (M.Tech) |
18 |
| |
Polymer Nano Technology |
18 |
| Orissa Engineering College, Bhubaneswar (36) |
Computer Science & Engineering |
18 |
| |
Mechanical System Design |
18 |
| IIIT, Bhubaneswar (25) |
Computer Science & Engineering |
25 |
| Krupajal, Bhubaneswar (72) |
Computer Science & Engineering |
18 |
| |
Power Electronics & Drives |
18 |
| |
Communication Engineering |
18 |
| |
Heat Power Engineering |
18 |
| CEB, Bhubaneswar (54) |
Computer Science & Engineering |
18 |
| |
Electrical & Communication |
18 |
| |
Thermal Engineering |
18 |
| C V Raman, Bhubaneswar (180) |
Industrial Engineering |
18 |
| |
Chemical Engineering |
18 |
| |
Computer Science & Engineering |
36 |
| |
Electrical (Power System) Engg |
18 |
| |
Electronics and Communication |
36 |
| |
Heat Power Engineering |
18 |
| |
IT |
18 |
| |
Mechatronics |
18 |
| Konark Institute, Bhubaneswar (36) |
Computer Science & Engineering |
18 |
| |
Electrical & Communication |
18 |
| NM Institute, Bhubaneswar (36) |
Power Electronics & Devices |
18 |
| |
Mechanical Engineering |
18 |
| Techno, Bhubaneswar (36) |
ECE |
18 |
| |
EEE |
18 |
| Gandhi Engineering College, Bhubaneswar (36) |
Computer Science & Engineering |
18 |
| |
Electrical & Communication |
18 |
| GITA, Bhubaneswar (36) |
Electrical / Electrical & Elex |
18 |
| |
Mechanical Engineering |
18 |
| Silicon, Bhubaneswar (72) |
Computer Sc & Engineering |
18 |
| |
Electrical / Electrical & Elex |
18 |
| |
Electronics &Telecommunication |
36 |
| GIET, Gunupur (144) |
Applied Elex & Instrumentation |
18 |
| |
Computer Science & Engineering |
18 |
| |
Machine Design |
18 |
| |
Thermal Engineering / Heat Power Engg. |
18 |
| |
CAD/CAM |
18 |
| |
Electronics & Comm. Engg. |
18 |
| |
Industrial Engineering |
18 |
| |
Power Electronics Engg. |
18 |
| IMIT, Cuttack (18) |
IT |
18 |
| NIST, Berhampur (54) |
VLSI & Embedded System Design |
18 |
| |
Wireless Communication Technology |
18 |
| |
Electronics & Communication Engineering |
18 |
IIPM, Kansbahal (0)
|
Production Management |
|
IMMT Bhubaneswar (10)
|
Material Research Engineering |
10 |
| IIT Kharagpur, Bhubaneswar Center (50) |
Electrical Engineering (3yr weekend and after hrs M.Tech) |
25 |
| |
Electronics & Communication Engineering (3yr weekend & after hrs M.Tech) |
25 |
| Utkal University, Bhubaneswar (30*) |
Computer Science |
30 |
| |
M.E in Computer Sc and Eng with specialization in Knowledge Engineering |
* |
| KIIT University, Bhubaneswar (144*) |
Water Resource Engineering – Civil |
18* |
| |
Construction Engineering & Management |
18* |
| |
Electrical |
18* |
| |
Mechanical |
18* |
| |
Computer Science |
18* |
| |
Electronics & Telecommunication |
18* |
SOA University, Bhubaneswar (144*)
|
Computer Science & Eng. |
18* |
| |
Applied Electronics & Instrumentation Engg. – VLSI Design & Embedded System) |
18* |
| |
Mechanical Engg. – Thermal Engineering |
18* |
| |
Electrical Engg. — Power Electronics & Drives |
18* |
| |
Electronics & Telecommunication Engg. – Telecommunication System Engineering |
18* |
| |
IT |
18* |
CET, Bhubaneswar (107)
|
Computer Science & Engg |
13 |
| |
IT |
18 |
| |
Industrial Engineering & Management |
18 |
| |
Structural Engineering |
18 |
| |
VLSI & Embedded Systems |
10 |
| |
Mechanical System Design & Dynamics |
10 |
| |
M.Architecture |
20 |
ABIT, Cuttack (20)
|
M.Architecture |
20 |
NIT Rourkela (288)
|
Biotechnology & Medical Engineering |
18 |
| |
Ceramic Engineering |
18 |
| |
Chemical Engineering |
18 |
| |
Civil Engineering – Soil Mechanics & Foundation Engg |
18 |
| |
Civil Engineering – Structural Engineering |
18 |
| |
Computer Science & Engineering- Computer Sc |
18 |
| |
Computer Science & Engineering- Info. Security |
18 |
| |
Electrical Engineering – Electronics Systems & Communication |
18 |
| |
Electrical Engineering – Power control & Drives |
18 |
| |
Electronics & Communication Engineering – Telematics & Signal Processing |
18 |
| |
Electronics & Communication Engineering – VLSI Design & Embedded Systems |
18 |
| |
Mechanical Engineering – Machine Design & Analysis |
18 |
| |
Mechanical Engineering – Production Engineering |
18 |
| |
Mechanical Engineering – Thermal Engineering |
18 |
| |
Metallurgical & Materials Engineering |
18 |
| |
Mining Engineering |
18 |
VSSUT, Burla (152)
|
Communication System |
18 |
| |
Heat Power Engineering |
12 |
| |
Hydraulic & Irrigation Engineering |
18 |
| |
Machine Design & Analysis |
12 |
| |
Power system Engineering |
18 |
| |
Production Engineering |
12 |
| |
Structural Engineering |
13 |
| |
Transportation Engineering |
13 |
| |
Computer Science & Engg |
18 |
| |
Manufacturing Systems |
18 |
IGIT Sarang (54*)
|
Electrical – Power Electronics & Drives |
18* |
| |
Civil – Environmental Science & Engineering |
18* |
| |
Mechanical – Mechanical System Design |
18* |
| OUAT, Bhubaneswar (*) |
Agricultural Engineering |
* |
| Sambalpur University (20) |
Food Science & Technology |
20 |
| SUIIT, Sambalpur (24) |
Computer Science |
24 |
The * implies that I am not sure of the number. The number I have in that case may be a few years old. The above adds up to 1830+372* seats total. Out of which 1112+318* seats are in the greater Bhubaneswar (including Dhenkanal) area.
My guess is that majority of these M.Tech’s (at least 50-60%) would go into teaching. This should definitely help the faculty quality of the engineering colleges and programs in Odisha. In a few years IIT Bhubaneswar is going to start M.Tech. That would help the situation further.
July 16th, 2010
The report is available at http://dheorissa.in/DHE/pdf/FinalTaskforceReport.pdf. Although the report took into account many of my suggestions I am not completely happy with it. I plan to submit a separate individual addendum to it.
Please feel free to comment on the report. I may be able to take them into account in my planned addendum.
The executive summary of the report is as follows:
Task Force on Higher Education was constituted by the Government of Odisha on 7th October 2009 under the chairmanship of Prof. Trilochan Pradhan as requested by the Minister of Higher Education, Tourism and Culture, Sri Debi Prasad Mishra. The mandate of the Task Force was to prepare two annual plans for years 2010-11 and 2011-12, two five year perspective plans corresponding to the 12th and 13th plan periods respectively as well as a draft higher education policy. During a period of four months the Task Force completed eighteen interactive sessions, two State Level Workshops and five Regional workshops, one each in North, South, East, West and Central Regions of the State. In addition to this, sectoral consultations were organized with stakeholders of School and Mass Education, Technical, Medical, Agriculture and Management sectors. The suggestions of the members of the Task Force and citizens from all sectors of the civil society have been received through email, surface mail, written submission and discussions across the table. The Task Force has taken into consideration all these in the preparation of the report. The report embodies the collective endeavour of the members of the Task Force and the stakeholders of regional consultations.
The key recommendations of the Task Force are in three major areas, namely Restoration, Expansion and Consolidation covering the periods of 2010-12, 2012-17 and 2017-22 respectively. Expansion, inclusion and excellence have been the guiding principles of the deliberations of the consultations.
Key Recommendations
1. State Council of Higher Education (OSCHE): A State Council of Higher Education, in the lines of the NCHER, needs to be created. Financial provision must be made in the budget for creation of the council in the coming financial year. Many of the recommendations of the Task Force would be implemented by the OSCHE.
2. Delinking Higher Secondary (+2) from the ambit of Higher Education: The +2 classes need to be separated from the degree colleges. Budgetary support to augment infrastructure and funding from Rastriya Madhyamit Sikhsya Abhiyan (RMSA) may be used to make this a smooth transition.
3. Degree Colleges: All degree colleges should adopt semester system and choice based credit programmes. All vacant posts must be filled with permanent staff. Selected autonomous colleges may be made into branch campuses of universities. Teachers should be regularly evaluated to ensure accountability.
4. Universities: Model University Act. Statutes should be drafted so that universities may use their autonomy for better governance. All regular vacant positions of the universities should be filled up on a priority basis. Faculty need to be regularly evaluated to ensure accountability. Programmes of the universities need to be revamped and choice based credit system may be followed. Each university campus should have about 50 affiliated colleges and a few identified research centres. Each university must have up-to-date web site with all information about the university.
5. New State Universities and Branch Campuses: A number of new affiliating universities, unitary universities, branch campuses of existing universities, a new University of Management Education and a new State Open University have been recommended. Suggestions for locations of these institutions have been received in the consultation process after assessing the educational need. An expert committee may be formed to look in to these and come up with final locations based on the detailed project report based on feasibility.
6. Attract Private Edupreneurs: Private universities should be established through Acts passed by the state legislatures.
7. Set up Research Centres: Establishment of research centers of excellence in various areas of local relevance must be pursued and these should be affiliated with the existing universities and institutions of national importance such as IIT, NISER, IIIT etc. Central funding for the same must be vigorously pursued to strengthen the existing and planned research centers.
8. Enhance Quality of Education: All plans for expansion must have a major thrust on enhancing quality of education. Hence due care must be taken for developing skills of teachers for enhancing teaching-learning transaction, creating conducive academic environment, improving the learning infrastructure, putting technology enabled learning into practice wherever possible, reforming examination systems, need-based revision of curriculum, etc.
9. Engineering Colleges: The existing state funded engineering colleges need to be revamped and their vacant positions need to be filled at the earliest. In addition 5 new State Institutes of Technologies have been proposed in the model of NIT with a focus on post-graduate education to mainly cater to the faculty needs in the state.
10. Medical Education: By 2022 each of the 13 undivided districts of Odisha should have one operational medical college, be it private, state funded, or PPP based. The three major medical colleges of the state should be upgraded to affiliating Health University status so that institutions in medical and allied subjects such as nursing and pharmacy etc. can be brought under their fold. A Rural Health Practitioner (RMP) program should be introduced in conjunction with all district hospitals to address the critical shortage of medical practitioners in the rural areas of the state.
11. Skill and Vocational Education: Odisha should create a community college system imparting skills that are in demand and providing opportunities for distance education, nonconventional career progression, developmental education, and continuous learning.
12. Education Development Fund: Financial mechanisms need to be devised so that all deserving students can access the opportunity to pursue higher education and finance should not be a constraint. Similarly no educational institution should suffer from lack of long-term low interest capital to pursue their goals of development. For this purpose, Education Development Fund should be set up along the lines of the Educational Financing Corporation being contemplated by the central government to enable infrastructure development as well as provide study loans.
13. From Mineral Resources to Human Resources: All private and public sector companies that are using Odisha’s mineral resources must be encouraged to contribute in creating higher education institutions.
14. Public Private Partnership: Encourage public-private partnership mode to set up institutes of higher learning. The proposed OSCHE needs to have a mechanism to monitor and regulate such efforts for the larger interest of all the stakeholders.
15. Financial Implication: The Task Force proposes that the State funding for Higher Education must increase to meet the cost of proposed expansion. The Task Force has estimated resource requirement of about 55000 crores over a period of 12 years to implement its recommendations at current prices. Similarly it is estimated that similar amounts may be generated through private sector projects and centrally funded projects.
16. Taking advantage of the Central Government Schemes: Taking advantage of the central government’s ambitious plan to achieve 30% GER by 2020, the state should seek all available resources under different schemes such as those for establishment of National Innovation University, IIM, National Institute of Design, Model colleges in Educationally Backward Districts, Tribal University etc. Besides all effort must be made to emphasize the special need of the state to develop its infrastructure in the remote tribal areas and priority funding must be.
Phases of Implementation
The Task Force proposes the following plan for implementation of the above recommendations:
i. Restoration and Preparation for Expansion (2010-12)
a. Separation of +2 from higher education and integration in School Education
b. Filling up of vacancies in regular positions
c. Setting up of Model colleges in educationally backward districts
d. Initiate the establishment State Council of Higher Education and other legislative
actions needed to carry out the recommendations.
e. Set up communication laboratories and high speed broad band internet access
f. Set up Management Information System and e-admission
g. Prepare ground for rapid expansion
ii. Rapid Expansion (2012-17)
a. Set up new affiliating Universities and institutions
b. Set up Unitary Universities by up-gradation of existing institutions
c. Set up branch campuses
d. Take initial steps for setting up research centres
iii. Consolidation (2017-22)
a. Expand Technology Enabled Learning
b. Strengthen quality initiatives
c. Strengthen governance through State Council (OSCHE)
d. Mobilisation of additional resource
The Task Force has taken note of the hopes and aspirations generated through the whole process of its activities. The major recommendations based on the inputs received from the stake-holders centre around three important areas: i) Creation of new institutions, ii) financing of higher education and iii) bringing governance reforms. Hence the Task Force recommends to set up a committee to advise the Government to work out further details.
June 25th, 2010
Following are excerpts from a report in tathya.in.
The Institute of Chartered Financial Analysts of India (ICFAI) University Bill received the green signal of the Odisha Legislative Assembly (OLA) today.
… Debi Prasad Mishra, Minister Higher Education piloted the Bill, which was introduced in the Monsoon Session of the Thirteenth Assembly.
Mr.Mishra agreed few changes in the Bill and it was passed after discussion.
… According to latest accommodation, two Members of the House and Secretary of the Department of Higher Education(DHE) will in the Board of Management(BOM) of the University.
Mr.Mishra also agreed to the proposal for granting concession to students belonging to ST, SC and OBC students.
Assembly asked the ICFAI authorities to prepare Fee Structure on the Guidelines of University Grants Commission (UGC) and other regulatory bodies.
Similarly the Endowment Fund will be raised to Rs.5 crore, which was Rs.3 crore.
… With the Bill cleared , now the Hyderabad-based ICFAI would invest Rs 150 crore in setting up a university in Odisha.
The university would have strength of about 1,500 students and offer courses in various disciplines like engineering, management, law, science and humanities.
… ICFAI has identified 30 acres of land between Bhubaneswar and Khurda for setting up its proposed university.
June 24th, 2010
From http://www.npti.in/about.html:
National Power Training Institute (NPTI) has been set up by the Government of India under the Ministry of Power, to function as the National Apex Body for Human Resources Development of Indian Power Sector. The Corporate Office of NPTI is located at NPTI Complex, Sector-33, Faridabad -121 003 (Haryana). It operates on an all India basis through its Institutes in the different regions/power zones of the country viz.. Neyveli. Durgapur, New Delhi, Nagpur, Guwahati, Faridabad and Bangalore.
From http://pmintpc.com/interface/about_us_overview.shtml:
The Power Management Institute (PMI) was set up by NTPC in recognition of the vital role that management development has to play, in the context of the challenges associated with the growth of the Indian Power Sector. The Institute is involved in the training and development of middle and senior level personnel not only from the power sector but from organizations outside the sector also.
… The institute’s integrated campus at Noida boasts of modern infrastructure and facilities.
Following is an excerpt from a Business Standard report in sify.com.
Keeping in view the huge manpower requirement for the upcoming power plants of the independent power producers (IPPs) in Orissa, the state government is mulling to set up a Power Management Institute on the lines of the National Power Training Institute (NPTI).
All the IPPs have assured their support to the state government for this institute. To implement the project, the state government would form a special purpose vehicle (SPV) with IPPs as stake holders.
The location, investment, intake capacity and other relevant details are yet to be worked out as things are at a preliminary stage.P K Jena, the state energy secretary, said, "The state government is planning to set up a power management institute on the lines of NPTI. The proposed institute is still at a conceptual stage and a concept note is being prepared by the state government in this connection."
"The power management institute will offer diploma as well as degree courses in engineering. The institute will primarily focus on various areas pertaining to the power sector", he added.
The objective behind setting up this institute is to prepare skilled and semi-skilled manpower for the upcoming power projects.It may be noted that as many as 27 IPPs have inked MoUs (Memorandum of Understanding) with the state government. All these 27 IPPs have a cumulative generation capacity of 32,420 MW.These power projects are set to generate around 50,000 direct jobs besides creating indirect employment for 150,000 people.
The page http://www.orissa.gov.in/energy/Mou-IPP/MoU_IPP1.htm lists 21 of the 27 MOUs that have been signed. We reproduce that list below.
|
SL
|
Name of the IPP
|
Proposed Capacity (in MW)
|
Capacity Enhanced (In MW)
|
Location
|
District
|
Date of MoU Signed
|
|
1
|
M/s KVK Nilachal Power (P) Limited
|
600
|
600
|
Gurudijhatia
|
Cuttack
|
Tuesday, September 26, 2006
|
|
2
|
M/s Monnet Power Company Limited
|
600
|
400
|
Nisha
|
Angul
|
Tuesday, September 26, 2006
|
|
3
|
M/s Sterlite Energy (P) Ltd.
|
2400
|
|
Bhurkamunda
|
Jharsuguda
|
Tuesday, September 26, 2006
|
|
4
|
M/s Tata Power Company Ltd.
|
1000
|
1000
|
Munduli Marthapur
|
Cuttack
|
Tuesday, September 26, 2006
|
|
5
|
M/s Calcutta Electricity Supply Corporation
|
1000
|
|
Neulapoi
|
Dhenkanal
|
Tuesday, September 26, 2006
|
|
6
|
M/s Bhusan Energy (P) Ltd.
|
2000
|
|
Nuahata
|
Angul
|
Tuesday, September 26, 2006
|
|
7
|
M/s Jindal India Thermal Power Limited
|
1000
|
200
|
Pirasahi
|
Angul
|
Tuesday, September 26, 2006
|
|
8
|
M/s Lanco Group Limited
|
1320
|
|
Badabandha
|
Dhenkanal
|
Tuesday, September 26, 2006
|
|
9
|
M/s Essar Power Limited
|
1000
|
|
Talcher
|
Angul
|
Tuesday, September 26, 2006
|
|
10
|
M/s Navabharat Power Private Ltd
|
1040
|
|
Khadagprasad
|
Dhenkanal
|
Friday, June 09, 2006
|
|
11
|
M/s GMR Energy Ltd
|
1000
|
|
Kamalanga
|
Dhenkanal
|
Friday, June 09, 2006
|
|
12
|
M/s Mahanadi Aban Power Company Ltd
|
1030
|
|
Talcher
|
Angul
|
Friday, June 09, 2006
|
|
13
|
M/s Visa Power Ltd.
|
1000
|
|
Brahmanbasta
|
Cuttack
|
Tuesday, September 26, 2006
|
|
14
|
M/s Aarti Steel Ltd
|
500
|
0
|
Ghantikhal
|
Cuttack
|
Saturday, February 07, 2009
|
|
15
|
M/s Astaranga Power Co. Ltd
|
2640
|
0
|
Astaranga
|
Puri
|
Saturday, February 07, 2009
|
|
16
|
M/s Chambal Infrastructure & Ventures Ltd
|
1200
|
0
|
Siaria
|
Dhenkanal
|
Saturday, February 07, 2009
|
|
17
|
M/s Ind-Bharat Energy(Utkal) Limited
|
700
|
0
|
Sahajbahal
|
Jharsuguda
|
Saturday, February 07, 2009
|
|
18
|
M/s Jindal Steel & Power Ltd
|
1320
|
0
|
Boinda
|
Angul
|
Saturday, February 07, 2009
|
|
19
|
M/s Kalinga Energy & Power Ltd
|
1000
|
0
|
Babuchakuli
|
Sambalpur
|
Saturday, February 07, 2009
|
|
20
|
M/s Sahara India Power Corporation Ltd
|
1320
|
0
|
Turla
|
Bolangir
|
Saturday, February 07, 2009
|
|
21
|
M/s Visaka Thermal Power(P) Ltd
|
1100
|
0
|
Bhandariphokhari
|
Bhadrak
|
Saturday, February 07, 2009
|
Status of the Progress made by the IPP as on 16-05-09–Click here
The progress status list mentions two coal blocks: Rampia coal block in the Ib Valley, Sundergarh and Mandakini coal block in Talcher, Angul. Most of the power plants are coming up in the Angul area. Based on the above the power management institute proposed by the Odisha government should be located either in the Angul area or the Jharsuguda area. But since the Angul area already has a government engineering college in Sarang near Talcher, the government must establish the proposed power management institute in Jharsuguda. A few other reasons in support of Jharsuguda as a location are:
- A lot of industries are coming up around Jharsuguda, but yet it does not have many government technical institutes. It has a government engineering school but no government engineering college.
- Jharsuguda is somewhat in the center of the industrial belt that spans from Rourkela to Sambalpur.
- Jharsuguda has excellent Rail connectivity and the second airport of the state is coming up there.
June 20th, 2010
Following is an excerpt from a report in pagalguy.com.
The Indian Institute of Technology (IIT), Kharagpur’s Vinod Gupta School of Management is starting two MBA programs for working executives at it Kolkata and Bhubhaneswar campuses. Working on a 3-year structure that will allow participants to work while they study, the courses are largely targeted towards the local population of each city they shall function in. While the Executive MBA at the Kolkata campus has a general management bent the Knowledge Industries MBA (KIMBA) at the Bhubhaneswar campus would focus on the IT and ITES sectors, explained EMBA coordinator Prof Gautam Sinha.
The intakes for both the programs would be 15 to 30 students each while the minimum eligibility will be three years of work experience and either an engineering education or post-graduate education in commerce, science or economics. More about the application system to the courses on the VGSoM website.
Prima facie, there are few differences between the EMBA and KIMBA except for a couple of core courses. The IT/ITES focused KIMBA has courses such as Technology Management and Services Management, which in the EMBA are replaced by International Management and IT & Business Applications Laboratory. Interestingly, the KIMBA has two courses on Financial Accounting while the EMBA has none. Both courses cost Rs 6 lakhs in fees, including a one-year international immersion program, which according to Prof Sinha may be carried out with one of IIT Kharagpur’s 99 tie-ups with various international institutions.
While both the courses look similar to 3-year part-time MBA courses in structure and content, Prof Sinha argues that several executive MBA courses across the world follow the part-time model. While that may be true, popular executive MBA programs in the USA or Europe wrap up in an year’s time, recognizing that the opportunity cost for working executives to stay away from work is high. To that extent, VGSOM’s Executive programs seem like 3-year part-time MBAs that give you an Executive MBA degree at the end, thus keeping you away from the stigma attached to the ‘part-time’ bit of part-time MBA.
Prof Sinha defends the three-year pattern of VGSOM’s Executive MBAs saying, “One-year or two-year programs are high pressure situations which might not be conducive for people with families.”
The links for the two programs are:
- E-MBA at Kolkata for all industries
- KI-MBA at Bhubaneswar for knowledge industries like Information Technology sector.
Note that earlier IIT Kharagpur also introduced 3 year weekend and after hours M.Tech programs in both cities. See https://www.orissalinks.com/archives/4118.
May 12th, 2010
The web page of this contest is at http://settlement.arc.nasa.gov/Contest/. The results of the 2010 page is at http://settlement.arc.nasa.gov/Contest/Results/2010/index.html. Following sentence is from that web page.
Prateeksha Das, Ispat English Medium School, Odisha, India’s entry "Paradise Reclaimed" won the inaugural Bruce Clark Memorial scholarship which goes to the top individual entry.
She is from the 11-12 grade.
Following is from Dharitri.

Last year a team from Bhubaneswar co-won the grand prize.
May 5th, 2010
Sources suggest that the Xavier University Bill is getting finalized and may be introduced in the Odisha assembly in the upcoming assembly session. There is plan that the proposed Xavier University (which will be established by the XIMB people) will have undergraduate programs including in Arts and Commerce.
This would be a Godsend. While Odisha now has top notch programs in Engineering (at IIT, NIT, VSSUT, CIPET), Science (NISER), Law (NLUO), Business (XIMB), Social Work (NISWASS), Public Health (AIPH, and soon IIPH) and Education (RIE), and soon will have a top notch program in fashion design (NIFT) and medicine (AIIMS-like Institute), it does not have top programs in Commerce and Arts. Thus the proposed Xavier University offering these programs will fill a huge lacuna. There are several reasons I believe that the Arts and Commerce programs at the proposed Xavier University will be top notch.
- They have track record in Odisha and India. Their XIMB is among the top ranked business schools in the country.
- The top ranked Arts and Commerce programs in the country include many other sister Jesuit institutions such as Loyola Colleges, St. Xavier’s colleges and St. Joseph’s colleges.
- Xavier University being a university will be able to modernize and revise its programs at will and thus will have advantage over other colleges that need to work with their universities. (Some of the top ranked colleges are now autonomous though.)
- Many of the other top ranked colleges are uni-disciplinary. Xavier University will be able to share faculty among multiple programs and thus able to create more multi-dimensional programs.
The proposed Xavier University offering top notch arts and commerce programs would help the other institutions to improve their arts and commerce programs and may even encourage other groups (such as KIIT and ITER) to establish good programs in Arts and commerce.
Thus the Odisha government should not delay and speed up the creation of Xavier University.
Following is from India Today’s 2009 list of top ranked Arts and Commerce programs in India.
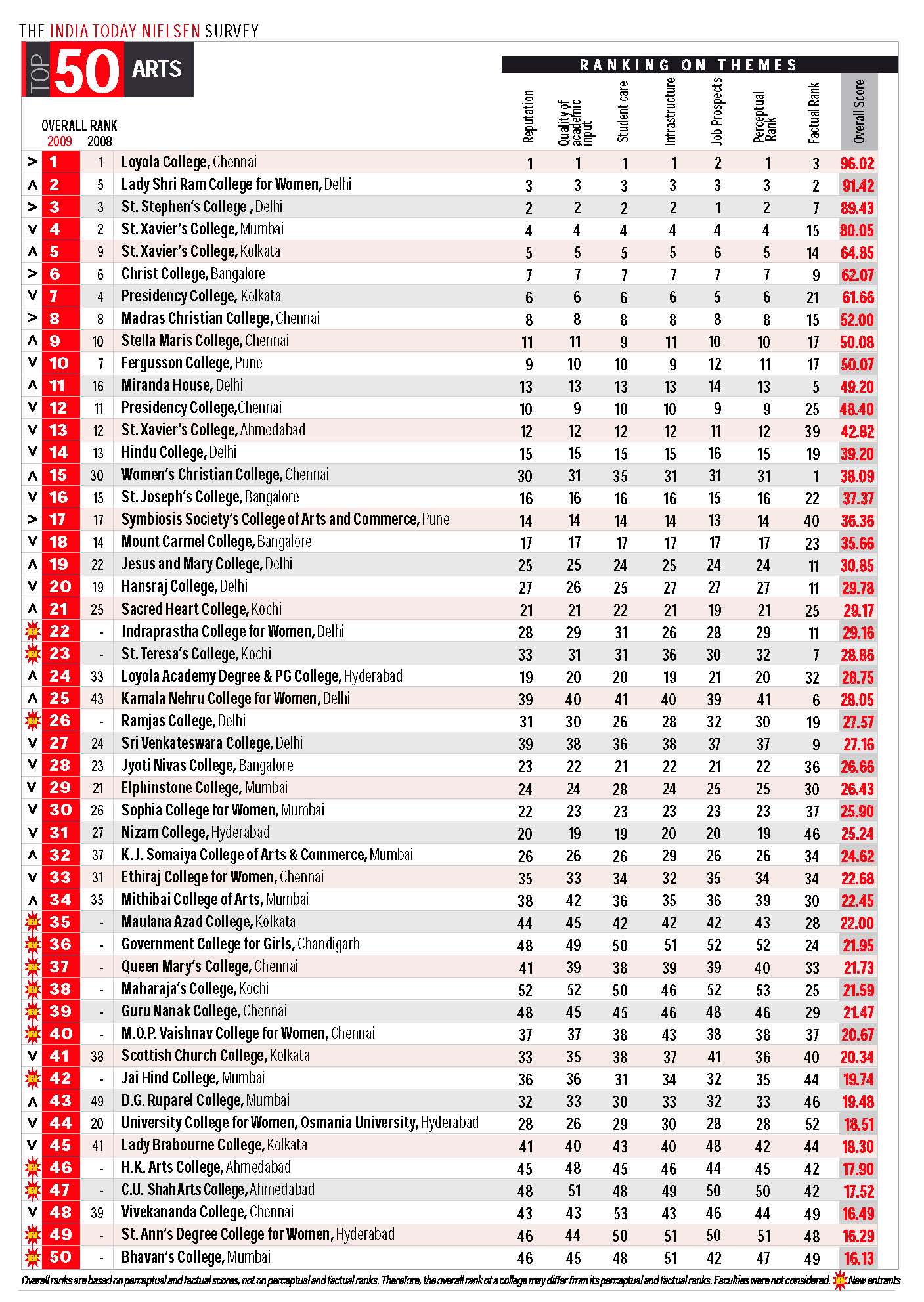
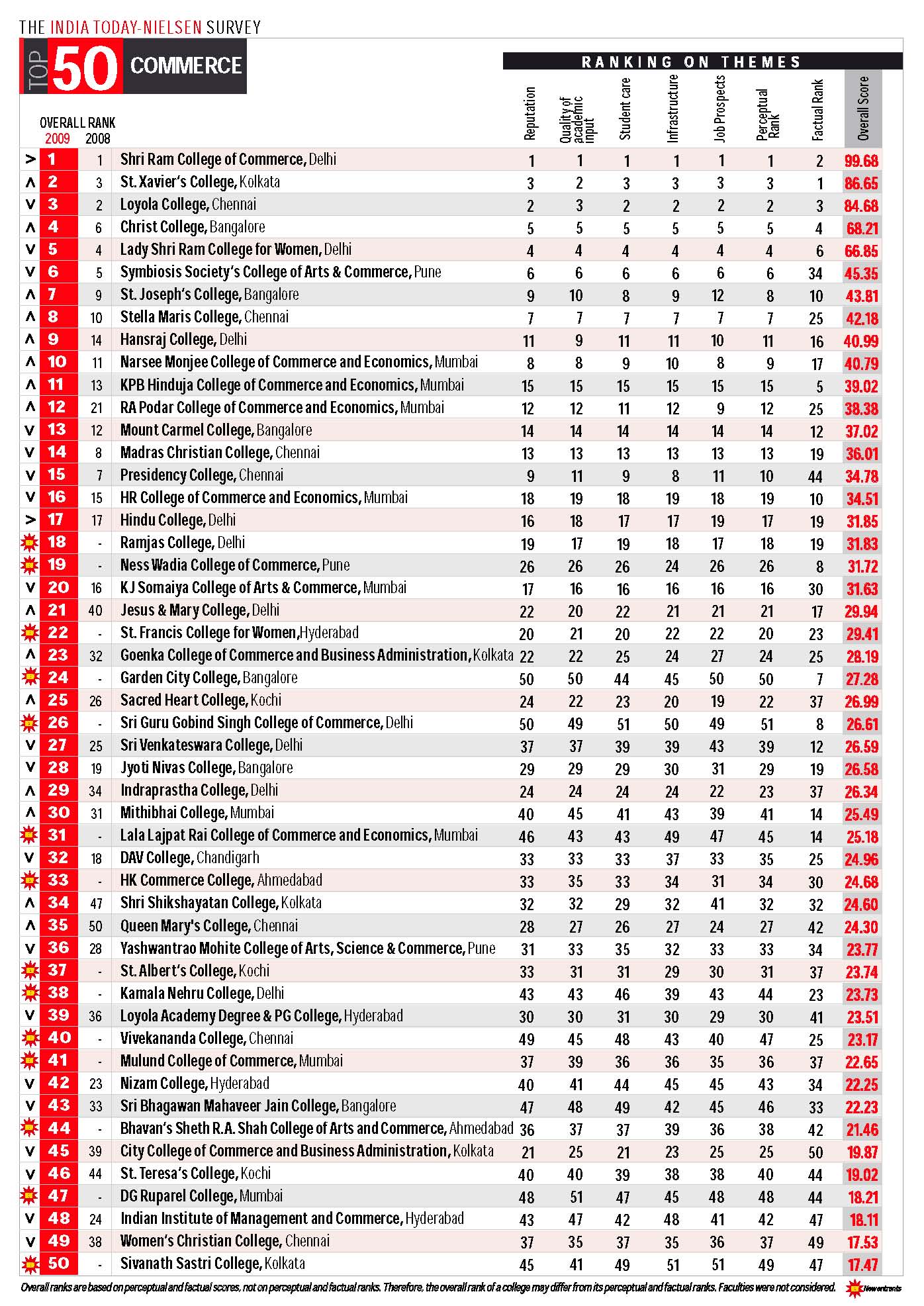
May 2nd, 2010
In 2008 Andhra created 3 new IIITs in rural areas of the state. These three IIITs at Basar, Nuzvid and RK Valley are the components of the newly established Rajiv Gandhi University of Knowledge Technologies. Following are excerpts from a report in Times of India that talks about hiring of faculty for these IIITs.
The institutes are going through a crisis at present due to inadequate faculty and lack of infrastructure because of which the state government has decided to reduce the intake of students by half — from 6,000 per year to 3,000 — from the coming academic year.
… “About 140 post-graduates from the five Indian Institutes of Technologies (IITs) and Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore have come forward to teach the rural students even though they have lucrative offers on hand from the corporate sector and international institutes,” said R V Raja Kumar, vice chancellor of the Rajiv Gandhi University for Knowledge Technologies under which the three institutes function.
At least half of the selected post-graduates and PhDs are Andhrites and have expressed their willingness to stay among the students and impart engineering education in the country, the VC said. Raja Kumar himself is an IITian from Kharagpur. “The hunt for talent will continue. We want to recruit post-graduates from the institutes of national and international repute in the country,” the VC said.
.. “This is for the first time in India that campus recruitment is being done by a university for the recruitment of the faculty. The response has been very encouraging and several post-graduates have volunteered to join the institutes located in remote areas,” said Raja Kumar.
In Odisha KIIT has been recruiting heavily from IITs. We reported on it in https://www.orissalinks.com/archives/2492. I hope the Odisha government engineering colleges, IIIT Bhubaneswar, SUIIT and VSSUT follow a similar approach and go for campus recruitment in the IITs.
The program at these IIITs in Andhra are different from programs anywhere else. See http://www.rgukt.in/program.html. They offer 6 year dual degree programs after the 10th class and take students mainly from the rural areas.
May 2nd, 2010
1. From a Times of India Report.
Targeting a production of about 500 tons of silk by 2020, Orissa government decided to set up a State Sericulture Research and Development Institute (SSRDI) for speedy growth of the sector.
2. From a Business Standard report:
Indo-US Collaboration for Engineering Education (IUCEE) — an initiative by the Pan IIT Alumni Association — has taken up a US co-guide PhD initiative wherein faculty members of Indian engineering institutes would be able to obtain PhDs in a four-year period, with the mentoring of distinguished US faculty.
… Under the arrangement, interested PhD candidates in India, who are currently teaching in engineering colleges, will identify and register with a PhD guide at an Indian PhD granting institution. The PhD candidate will identify his area of research interest.
If there appears to be matching of interests between an Indian PhD candidate and a US faculty, IUCEE will facilitate the process forward.
Also, the PhD candidate will make a trip to the US institution of the co-guide to ensure exposure to high quality research culture. The co-guide will also visit the Indian institution, to ensure adequate mentoring of the candidate.
… IUCEE is also exploring various avenues for requesting government of India to provide schemes for this purpose.
3. From a Times of India report:
Three of Maharashtra’s premier universities—Mumbai, Pune and Nagpur—will be split to create new universities.
…Spelling out some details, Tope said the University of Mumbai would be split into two campuses, with a pro vice-chancellor becoming the head of the new campus. The name, though, would not be altered, given Mumbai university’s iconic status, he added. He was replying to a discussion on the supplementary demands of his department.
… Maharashtra has also revived the plan to bring private universities into the state. Tope said that plans were afoot to help the corporate sector play a key role in the field of education. The Private University Act is being finalised in this connection, he pointed out.
April 16th, 2010
Following is an excerpt from a report in Times of India.
The MSC Ed, an integrated six-year course (12 semesters), introduced in 2008 is the right way to master teaching skills. Offering quality teacher education programmes is the Regional Institute of Education that include innovative pre-service and in-service teacher training programmes and relevant research, development and extension activities.
The institute started as Regional College of Education in 1963, changed the name in 1994. It is one of the five such institutions established by the National Council of Education Research and Training (NCERT), New Delhi. The other institutes are located at Ajmer, Bhopal, Bhubaneswar and Shilong.
Prior to the six-year course, there was a two-year MSC Ed course for those who had completed BSC Ed, said Regional Institute of Education Principal GT Bhandage. "It had a good response and the students from all over the country would appear for the entrance exam. This course was conceived essentially to meet the demand of the higher secondary level in specific subjects like physics, chemistry and mathematics. Students who have passed out from this course were absorbed by Navodaya and Kendriya Vidyalaya," added Bhandage.
In 2008, MSC Ed course was introduced after completion of II PUC or equivalent. The idea was to catch them young and train them with pedagogic skills and develop adequate content competency crucial to a teacher education programme, said Bhandage.
The six years integrated course is a combination of BSc and MSC. The first four years, students study physics, chemistry and mathematics while in fifth and final year they can choose a specialization subject.
After completion of the course one can get into Higher Secondary Schools or can do research.
… The admissions are made on all India basis through an entrance exam. The selection will be based on the performance in the qualifying exam and entrance exam.
For details log on to www.riemysore.ac.in or call 514515/ 2514095.
RIE Mysore has a website at www.riemysore.ac.in. I have not been able to find a web site for RIE Bhubaneswar. I wonder if RIE Bhubaneswar offers such a course.
Considering the implementation of RTE, there is a big need for more and better trained teachers and educational administrators (headmasters, principals, vice-principals, etc.). To achieve that the government of India should upgrade the RIEs to National Institutes of Education and make them Institutions of National Importance. This will attract the attention of more good students towards a teaching and teaching administration career. The government should incraese the number of seats and number of programs in these institutes and intrdoce programs for creating top-notch Educational administrators.
April 14th, 2010
Update: Following are excerpts from a follow-up Telegraph report which mentions about the committee’s recommendation to have wide-spread consultations before making the changes.
But it has advised caution in implementing the reforms. The panel has suggested detailed consultations and workshops with the state governments, other top engineering institutions like the National Institutes of Technology, and private universities.
The recommendations of the panel can be fine-tuned based on the outcome of the consultations, the team led by IIT Kharagpur director Damodar Acharya has suggested. The panel is likely to meet soon and may draw up a schedule for the consultations at that meeting.
… At a meeting of the panel in Chennai on March 16 with representatives of state and central school boards, some participants suggested that rural students be given more opportunities than urban students. The participants proposed two attempts for urban students and three for rural students.
The panel and the HRD ministry will also need to convince state governments that the move to end state-specific engineering tests is not against their interests.
Following is an excerpt from a report in Telegraph.
… The panel, appointed by human resource development minister Kapil Sibal, has recommended replacing the four-decade-old IIT-Joint Entrance Examination (JEE) and myriad other engineering entrance examinations with a common test modelled on the US-based scholastic aptitude test (SAT).
The panel has suggested that the IITs accord a 70 per cent weightage to board examination scores in picking students, ..
Scores in the common aptitude test that will replace the IIT-JEE will contribute the remaining 30 per cent weightage in determining which candidates are selected, the panel has recommended.
Unlike the current engineering entrance examinations including the IIT-JEE, the common aptitude test will not have questions on physics, chemistry and math, but will test students’ powers of logical reasoning and communication skills.
If the recommendations are accepted, the IITs will for the first time admit students based more on their board examination marks than on their performance in a special entrance test.
…The minister had announced in February that he was setting up a panel under IIT Kharagpur director Damodar Acharya to study proposed reforms to the IIT-JEE. The panel was appointed in March, with the directors of the IITs in Mumbai, Roorkee and Chennai as the other members.
… The panel has recommended that the government develop a Comprehensive Weighted Performance Index (CWPI) to calculate a student’s overall score based cumulatively on his performance in the board examinations and in the common aptitude test. The report appears principally based on discussions at a meeting held with other government representatives, including Central Board of Secondary Education chairman Vineet Joshi and select state representatives in Chennai on March 16.
The HRD ministry is already working towards a plan to introduce a common high school curriculum in the sciences and math, cutting across the 35 boards — central and state — that govern Indian school education.
The common curriculum would make easier a comparison between the board examination scores of students from schools affiliated to different central and state government boards, Joshi had told the meeting.
The CWPI proposed by the panel is aimed at normalising any differences that remain between difficulty levels of school-leaving examinations under different boards.
There is a big danger that the above approach will make the XIIth exams a high stakes affair and bring it under the microscope with every aspect of it being scrutinized and judged by everyone. Most coaching classes may reinvent themselves and start coaching how to score more marks in the XIIth exam and the proposed SAT type exam. This approach may bring in bias favoring students from families with educated parents. English being a compulsory subject in XIIth, this may put students in rural areas and other areas where English is less used at a disadvantage.
So one has to wait and see how this will pan out.
My guess is if the above idea is adopted, it will go through some changes such as specific types of colleges may be allowed to give different weight to Class XII marks in different subjects. Some may introduce interviews or other tests.
One change that should be made is that when possible specialty branches should not be assigned to most students (say 70-80% in any college/institute) immediately after they join a college/institute after the XIIth. That should be determined after a year in that college/institute based on the performance in that year. This will make the class XII exam less cutthroat and ensure that students after they get into a college/institute continue to give importance to academics.
One alternative idea may to test the proposed idea (of using class XIIth marks) on 50% of the seats for a few years before deciding whether to completely abandon the current approach or not.
April 14th, 2010
(Request to readers: If you know of private state universities not listed below and not in the UGC list mentioned below, please add a link in the comment. We will update this page.)
In this page we will collect information regarding private state universities in India. By private state universities we mean privately managed universities that are establish by an act in the assembly of various states of India. These are different from the deemed universities.
The list at UGC date June 2009 is at http://www.ugc.ac.in/notices/updatedpriuniver.pdf. We also listed them at https://www.orissalinks.com/archives/2782. My guess is that these private universities which have been created by state acts have UGC approval. We have come across many other private universities which have been created by state acts which are not in this list; some of them were created by state acts after June 2009.
We start with Odisha: Odisha has passed state acts for two private universities:
- Vedanta University
- Sri Sri University
Odisha has introduced an act for ICFAI university. It has been discussed and tabled in the assembly. As of writing this, It is yet to be passed by the Odisha assembly.
Chhatisgarh: The UGC list of June 2009 lists two private universities. (i) CV Raman in Bilaspur and (ii) MATS in Raipur
Gujarat: .The UGC list of June 2009 lists five private universities. (i) DAIICT Gandhinagar (ii) Ganpat, Mehsana (iii) Kadi Sarva, Gandhinagar (iv) Nirma, Ahmedabad (v) Pandit Deendayal Petroleum U, Gandhinagar
Himachal Pradesh: It passed an umbrella private university act in 2006. The UGC list of June 2009 lists two private universities. (i) Chitkara University, Solan (ii) Jaypee, Solan. Besides them following are some new ones.
Jharkhand:
Karnataka: The UGC list of June 2009 does not have any university from Karnataka. However, since then the following has been passed.
Madhya Pradesh: It passed an umbrella private university act in 2007.
Maharashtra: From a TOI report.
Maharashtra has also revived the plan to bring private universities into the state. Tope said that plans were afoot to help the corporate sector play a key role in the field of education. The Private University Act is being finalised in this connection, he pointed out.
Meghalaya: The UGC list of June 2009 lists two private universities. (i) Martin Luther Christian (ii) Techno Global.
Mizoram: The UGC list of June 2009 lists one private university. (i) ICFAI
Nagaland: The UGC list of June 2009 lists one private university. (i) Global Open
Punjab: The UGC list of June 2009 lists one private university. (i) Lovely Professional U.
Rajasthan: It has an umbrella private university act (enacted in 2005) to facilitate creation of private universities. There are 11 private state universities in Rajasthan in the UGC list of June 2009. (i) Bhagwant University, Ajmer (ii) Jagannath University, Jaipur (iii) Jaipur National University, Jaipur. (iv) Jyoti Vidyapeeth Women’s University, Jaipur. (v) Mewar University, Chittorgarh. (vi)
NIMS University, Jaipur. (vii) Sir Padmapat Singhania University, Jhunjhunu. (viii) Singhania University, Jhunjunu. (ix) Suresh Gyan Vihar University, Jaipur. (x) Jodhpur National University, Jodhpur (xi) Amity University, Jaipur
Beyond those 11, some of the new ones not in that list are:
Sikkim: The UGC list of June 2009 lists two private universities.(i) Eastern Institute for Integrated Learning in Management University, Jorethang. (ii) Sikkim- Manipal University of Health, Medical & Technological Sciences, Gangtok.
Tripura: The UGC list of June 2009 lists one private university. (i) ICFAI
UP: The UGC list of June 2009 lists eight private universities.(i) Amity University, NOIDA (ii) Integral University, Lucknow. (iii) Jagadguru Rambhadracharya Handicapped University, Chitrakoot Dham. (iv) Mangalayatan University, Aligarh (v) Mohammad Ali Jauhar University, Rampur. (vi) Sharda University, Gautam Budh Nagar. (vii) Swami Vivekanand Subharti University, Meerut. (viii)
Teerthanker Mahaveer Univesity, Moradabad.
Uttarakhand: The UGC list of June 2009 lists six private universities.(i) Dev Sanskrit Vishwavidyalaya, Haridwar. (ii) Doon University, Dehradoon. (iii) Himgiri Nabh Vishwavidyalaya, Dehradun. (iv) ICFAI Dehradun (v) University of Petroleum and Energy Studies, Dehradun. (vi) University of Patanjali, Haridwar.
West Bengal: The UGC list of June 2009does not have any from West Bengal. However, the following has been passed by West Bengal assembly since then.
- Dhirubhai Ambani Institute of Information and Communication Technology, Kalyani
In regards to umbrella private university bills, as per http://www.academics-india.com/SC%20judgement.htm the Supreme court in
Prof. Yashpal & Anr. Vs. State of Chhattisgarh & Ors.
Coram: CJI ,G. P. Mathur , P.K. Balasubramanyan 11/ 02/ 2005
CASE NO.: Writ Petition (civil) 19 of 2004
PETITIONER: Prof. Yashpal & Anr.
RESPONDENT:State of Chhattisgarh & Ors.
DATE OF JUDGMENT: 11/02/2005
BENCH:CJI,G. P. Mathur & P.K. Balasubramanyan
has reiterated (see point 36) UGC rules that say:
3.1 Each private University shall be established by a separate State Act and shall conform to the relevant provisions of the UGC Act, 1956, as amended from time to time.
3.2 A private university shall be a unitary university having adequate facilities for teaching, research, examination and extension services.
The following table summarizes the private and deemed universities in various states of India. The data regarding deemed universities is from http://pib.nic.in/release/release.asp?relid=50713. Since the HRD minister Mr. Sibal has said that the deemed university system will vanish, most of the private deemed universities will become private state universities.
| State |
# private universities in June 2009 |
# deemed universities |
# private universities in pipeline that we know of (work in progress) |
Total |
| Andhra Pradesh |
0 |
7 |
|
7 |
| Arunachal Pradesh |
0 |
1 |
|
1 |
| Bihar |
0 |
2 |
|
2 |
| Chhatisgarh |
2 |
0 |
|
2 |
| Gujarat |
2 |
5 |
|
7 |
| Haryana |
0 |
5 |
|
5 |
| Himachal Pradesh |
2 |
0 |
5 |
7 |
| Jharkhand |
|
2 |
1 |
3 |
| Karnataka |
|
15 |
1 |
16 |
| Kerala |
|
2 |
|
2 |
| Madhya Pradesh |
1 |
3 |
|
4 |
| Maharashtra |
|
21 |
|
21 |
| Meghalaya |
2 |
|
|
2 |
| Mizoram |
1 |
|
|
1 |
| Nagaland |
1 |
|
|
1 |
| Orissa |
|
2 |
3 |
5 |
| Pondicherry |
|
2 |
|
2 |
| Punjab |
1 |
3 |
|
4 |
| Rajasthan |
11 |
8 |
4 |
23 |
| Sikkim |
2 |
|
|
2 |
| Tamil Nadu |
|
29 |
|
29 |
| Tripura |
2 |
|
|
2 |
| Uttarkhand |
6 |
4 |
|
10 |
| Uttar Pradesh |
8 |
10 |
|
18 |
| West Bengal |
|
1 |
1 |
2 |
| Delhi |
|
11 |
|
11 |
April 10th, 2010
Next Posts
Previous Posts





